Coding Interview.
Classification
03.数组中的重复数字 03.1找出数组中重复的数字 题目描述 在一个长度为 n 的数组里的所有数字都在 0 到 n-1 的范围内。数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字是重复的,也不知道每个数字重复几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 Input: {2,3,1,0,2,5,3} Output: 2
大致思路 对于这种数组元素在 [0, n-1] 范围内的问题,可以将值为 i 的元素调整到第 i 个位置上进行求解。本题要求找出重复的数字,因此在调整过程中,如果第 i 位置上已经有一个值为 i 的元素,就可以知道 i 值重复。
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class Solution { public boolean duplicate (int numbers[],int length,int [] duplication) { int temp; if (length <= 0 || numbers == null ) return false ; for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++){ while (numbers[i] != i){ if (numbers[i] != numbers[numbers[i]]){ temp = numbers[numbers[i]]; numbers[numbers[i]] = numbers[i]; numbers[i] = temp; } else { duplication[0 ] = numbers[i]; return true ; } } } return false ; } }
03.2不修改数组找出重复的数字 题目描述 在一个长度为 n + 1 的数组里的所有数字都在 1到 n 的范围内。数组中至少有一个数字重复,请找出任意一个重复的数字但不能修改输入的数组。
大致思路 利用二分法 每次将1-n的数字分成1-m和m+1到n 若1-m的数字数目超过m则一定存在重复的数字 否则 m+1到n存在重复数字 接着再不断将两边区间继续二分直到找到一个重复数字
但无法保证找出所有重复数字 eg.1-2之间有两个2 这个范围数字也出现2次
04.二维数组中的查找 题目描述 给定一个二维数组,其每一行从左到右递增排序,从上到下也是递增排序。给定一个数,判断这个数是否在该二维数组中。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Consider the following matrix: [ [1, 4, 7, 11, 15], [2, 5, 8, 12, 19], [3, 6, 9, 16, 22], [10, 13, 14, 17, 24], [18, 21, 23, 26, 30] ] Given target = 5, return true . Given target = 20, return false .
大致思路 该二维数组中的一个数,小于它的数一定在其左边,大于它的数一定在其下边。因此,从右上角开始查找,就可以根据 target 和当前元素的大小关系来缩小查找区间,当前元素的查找区间为左下角的所有元素。
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution { public boolean findNumberIn2DArray (int [][] matrix, int target) { if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0 ].length == 0 ) return false ; int row = matrix.length,column = matrix[0 ].length; int r = 0 ,c = column - 1 ; while (r <= row-1 && c >= 0 ){ if (matrix[r][c] == target) return true ; else if (matrix[r][c] > target) c--; else r++; } return false ; } } public class Solution { public boolean Find (int target, int [][] array) { for (int i=0 ;i<array.length;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<array[0 ].length;j++){ if (target<array[0 ][0 ]){ return false ; } else if (target>array[i][j]){ continue ; } else if (target==array[i][j]){ return true ; } } } return false ; } }
05.替换空格 题目描述 将一个字符串中的空格替换成 “%20”。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 Input: "A B" Output: "A%20B"
大致思路
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public String replaceSpace (String s) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer (); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { if (s.charAt(i) == ' ' ) { sb.append("%20" ); continue ; } sb.append(s.charAt(i)); } return sb.toString(); } }
06.从尾到头打印链表 题目描述 从尾到头反过来打印出每个结点的值。
输入输出 1 2 输入:head = [1,3,2] 输出:[2,3,1]
大致思路 利用栈顺序push之后再pop / 利用递归 / 利用头插法 link
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 class Solution {public int [] reversePrint(ListNode head) { if (head == null ){ return new int [0 ]; } Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); while (head != null ){ stack.push(head.val); head = head.next; } int n = stack.size(); int [] ans = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ;i < n;i ++ ){ ans[i] = stack.pop(); } return ans; } } public class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead (ListNode listNode) { ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (listNode == null ) { return res; } addElement(listNode, res); return res; } private void addElement (ListNode listNode, ArrayList<Integer> res) { if (listNode.next != null ) { addElement(listNode.next, res); } res.add(listNode.val); } } class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ){ return head; } ListNode subListHead = reverseList(head.next); head.next.next = head; head.next = null ; return subListHead; } } class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { if (head == null ){ return null ; } ListNode p1 = head; ListNode p2 = head.next; p1.next = null ; while (p2 != null ){ ListNode temp = p2.next; p2.next = p1; p1 = p2; p2 = temp; } return p1; } }
07.重建二叉树 题目描述 根据二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7] 中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] 返回 3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7
大致思路 前序遍历的第一个值为根节点的值,使用这个值将中序遍历结果分成两部分,左部分为树的左子树中序遍历结果,右部分为树的右子树中序遍历的结果。然后分别对左右子树递归地求解。
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 class Solution { public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder, int [] inorder) { if (preorder.length == 0 || inorder.length == 0 ) { return null ; } int n = preorder.length; return constructBinaryTree(preorder, 0 , n - 1 , inorder, 0 , n - 1 ); } private TreeNode constructBinaryTree (int [] pre, int startPre, int endPre, int [] in, int startIn, int endIn) { TreeNode node = new TreeNode (pre[startPre]); if (startPre == endPre) { if (startIn == endIn) { return node; } throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Invalid input!" ); } int inOrder = startIn; while (in[inOrder] != pre[startPre]) { ++inOrder; if (inOrder > endIn) { new IllegalArgumentException ("Invalid input!" ); } } int len = inOrder - startIn; if (len > 0 ) { node.left = constructBinaryTree(pre, startPre + 1 , startPre + len, in, startIn, inOrder - 1 ); } if (inOrder < endIn) { node.right = constructBinaryTree(pre, startPre + len + 1 , endPre, in, inOrder + 1 , endIn); } return node; } } class Solution { public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder, int [] inorder) { int n = preorder.length; int m = inorder.length; if (m == 0 || m == 0 || m != n){ return null ; } Map<Integer, Integer> indexMap = new HashMap <>(n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ indexMap.put(inorder[i], i); } return constructTree(preorder, 0 , n-1 , indexMap, 0 , n-1 ); } private TreeNode constructTree (int [] pre, int startPre, int endPre, Map<Integer, Integer> indexMap, int startIn, int endIn) { if (startPre > endPre || startIn > endIn){ return null ; } int rootval = pre[startPre]; TreeNode node = new TreeNode (rootval); int rootIndex = indexMap.get(rootval); node.left = constructTree(pre, startPre+1 , rootIndex-startIn+startPre, indexMap, startIn, rootIndex-1 ); node.right = constructTree(pre, rootIndex-startIn+startPre+1 , endPre, indexMap, rootIndex+1 , endIn); return node; } }
08.二叉树的下一个结点 题目描述 给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。
大致思路
该结点有右子树 则是其右子树的最左节点
该结点无右子树
2.1 若他是一个左孩子 则是其父
2.2 若他是一个右孩子 则一直追溯其祖先直到是左子 其父就是
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public class Solution { public TreeLinkNode GetNext (TreeLinkNode pNode) { if (pNode == null ){ return null ; } if (pNode.right != null ){ TreeLinkNode node = pNode.right; while (node.left != null ){ node = node.left; } return node; } else { while (pNode.next != null ){ TreeLinkNode parent = pNode.next; if (parent.right != pNode){ return parent; } pNode = pNode.next; } } return null ; } }
09.栈和队列的实现 09_1 用两个栈实现队列 题目描述 用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的 Push 和 Pop 操作。 队列中的元素为 int 类型。
大致思路 牛客网 push:
把数据push进S1
pop:
若S2空S1不空 把S1pop出来push进S2
若S2空S1不空 报错
把S2pop出来
leetcode appendTail: //务必让新元素放在S1栈底
若S1非空 将S1全部pop出来 push进S2
把新的push进S1
若S2非空 将S2全部pop出来push进S1
size+1
deleteHead:
若size==0 返回-1
若size>0 size– 再把S1pop出来
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 import java.util.Stack;public class Solution { Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack <Integer>(); Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack <Integer>(); public void push (int node) { stack1.push(node); } public int pop () { if (stack2.isEmpty()){ if (stack1.isEmpty()){ return -1 ; } while (!stack1.isEmpty()){ stack2.push(stack1.pop()); } } return stack2.pop(); } } class CQueue { Stack<Integer> stack1; Stack<Integer> stack2; int size; public CQueue () { stack1 = new Stack <Integer>(); stack2 = new Stack <Integer>(); size = 0 ; } public void appendTail (int value) { while (!stack1.isEmpty()) { stack2.push(stack1.pop()); } stack1.push(value); while (!stack2.isEmpty()) { stack1.push(stack2.pop()); } size++; } public int deleteHead () { if (size == 0 ) { return -1 ; } size--; return stack1.pop(); } }
09_2 用队列实现栈 题目描述 使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
注意:
大致思路 使用辅助队列 思想大致相同
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 class MyStack { Queue<Integer> queue; Queue<Integer> help_queue; public MyStack () { queue = new LinkedList <>(); help_queue = new LinkedList <>(); } public void push (int x) { queue.add(x); } public int pop () { while (queue.size() > 1 ){ help_queue.add(queue.poll()); } int result = queue.poll(); while (!help_queue.isEmpty()){ queue.add(help_queue.poll()); } return result; } public int top () { while (queue.size() > 1 ){ help_queue.add(queue.poll()); } int result = queue.poll(); help_queue.add(result); while (!help_queue.isEmpty()){ queue.add(help_queue.poll()); } return result; } public boolean empty () { return queue.isEmpty(); } }
10.斐波那契数列 题目描述 大致思路 java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 public class Solution { public int Fibonacci (int n) { if (n < 2 ){ return n; } return Fibonacci(n-1 )+Fibonacci(n-2 ); } } class Solution { public int fib (int n) { if (n<2 ){ return n; } int [] res =new int [n+1 ]; res[0 ] = 0 ; res[1 ] = 1 ; for (int i=2 ; i<=n; ++i){ res[i] = res[i-1 ] + res[i-2 ]; } return res[n]; } } public class Solution { public int JumpFloorII (int target) { if (target <= 2 ){ return target; } else { return JumpFloorII(target - 1 ) * 2 ; } } } public class Solution { public int RectCover (int target) { if (target <= 2 ){ return target; } int [] res = new int [target+1 ]; res[1 ] = 1 ; res[2 ] = 2 ; for (int i = 3 ; i<=target; i++){ res[i] = res[i-1 ] + res[i-2 ]; } return res[target]; } }
11.旋转数组的最小数字 题目描述 把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个非递减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。
输入输出 例如数组{3,4,5,1,2}为{1,2,3,4,5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。
大致思路 利用一个二分法提取一个中间指针不断缩小范围
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 class Solution { public int minArray (int [] numbers) { if (numbers.length <= 0 ){ return 0 ; } int index1 = 0 ; int index2 = numbers.length -1 ; int indexMid = index1; while (numbers[index1] >= numbers[index2]){ if (index2 - index1 == 1 ){ indexMid = index2; break ; } indexMid = (index1 + index2)/2 ; if (numbers[index1] == numbers[index2] && numbers[indexMid] == numbers[index1]){ return minInorder(numbers, index1, index2); } if (numbers[indexMid] <= numbers[index2]){ index2 = indexMid; } else if (numbers[indexMid] >= numbers[1 ]){ index1 = indexMid; } } return numbers[indexMid]; } private int minInorder (int [] nums,int index1, int index2) { int result = nums[index1]; for (int i = index1 + 1 ;i <= index2; ++i){ if (result > nums[i]){ result = nums[i]; } } return result; } } class Solution { public int minArray (int [] numbers) { int i = 0 ,j = numbers.length - 1 ; while (i < j){ int m = (i + j) / 2 ; if (numbers[m] > numbers[j]) i = m + 1 ; else if (numbers[m] < numbers[j]) j = m; else j--; } return numbers[i]; } }
12.矩阵中的路径 题目描述 判断在一个矩阵中是否存在一条包含某字符串所有字符的路径。路径可以从矩阵中的任意一个格子开始,每一步可以在矩阵中向上下左右移动一个格子。如果一条路径经过了矩阵中的某一个格子,则该路径不能再进入该格子。
大致思路 使用回溯法(backtracking)进行求解,它是一种暴力搜索方法,通过搜索所有可能的结果来求解问题。回溯法在一次搜索结束时需要进行回溯(回退),将这一次搜索过程中设置的状态进行清除,从而开始一次新的搜索过程。
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 public class Solution { public boolean hasPath (char [] matrix, int rows, int cols, char [] str) { boolean visitFlags[] = new boolean [matrix.length]; for (int row = 0 ; row < rows; row++) { for (int col = 0 ; col < cols; col++) { if (hasPathCore(matrix, rows, cols, row, col, str, 0 , visitFlags)) return true ; } } return false ; } boolean hasPathCore (char [] matrix, int rows, int cols, int row, int col, char [] str, int k, boolean [] visitFlags) { int index = row * cols + col; if (row < 0 || col < 0 || row >= rows || col >= cols || visitFlags[index] || matrix[index] != str[k]) return false ; visitFlags[index] = true ; if (k == str.length - 1 ) return true ; k++; if (hasPathCore(matrix, rows, cols, row + 1 , col, str, k, visitFlags) || hasPathCore(matrix, rows, cols, row - 1 , col, str, k, visitFlags) || hasPathCore(matrix, rows, cols, row, col + 1 , str, k, visitFlags) || hasPathCore(matrix, rows, cols, row, col - 1 , str, k, visitFlags)) return true ; visitFlags[index] = false ; return false ; } } class Solution { public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { char [] words = word.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i < board.length; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < board[0 ].length; j++) { if (dfs(board, words, i, j, 0 )) return true ; } } return false ; } boolean dfs (char [][] board, char [] word, int i, int j, int k) { if (i >= board.length || i < 0 || j >= board[0 ].length || j < 0 || board[i][j] != word[k]) return false ; if (k == word.length - 1 ) return true ; char tmp = board[i][j]; board[i][j] = '/' ; boolean res = dfs(board, word, i + 1 , j, k + 1 ) || dfs(board, word, i - 1 , j, k + 1 ) || dfs(board, word, i, j + 1 , k + 1 ) || dfs(board, word, i , j - 1 , k + 1 ); board[i][j] = tmp; return res; } }
13.机器人的运动范围 题目描述 地上有一个m行和n列的方格。一个机器人从坐标0,0的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左,右,上,下四个方向移动一格,但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于k的格子。 例如,当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格(35,37),因为3+5+3+7 = 18。但是,它不能进入方格(35,38),因为3+5+3+8 = 19。请问该机器人能够达到多少个格子?
大致思路 回溯法+深度优先搜索
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public class Solution { public int movingCount (int threshold, int rows, int cols) { if (threshold < 0 || rows < 1 || cols < 1 ) { return 0 ; } boolean [] visited = new boolean [rows * cols]; return getCount(threshold, 0 , 0 , rows, cols, visited); } private int getCount (int threshold, int i, int j, int rows, int cols, boolean [] visited) { if (check(threshold, i, j, rows, cols, visited)) { visited[i * cols + j] = true ; return 1 + getCount(threshold, i - 1 , j, rows, cols, visited) + getCount(threshold, i + 1 , j, rows, cols, visited) + getCount(threshold, i, j - 1 , rows, cols, visited) + getCount(threshold, i, j + 1 , rows, cols, visited); } return 0 ; } private boolean check (int threshold, int i, int j, int rows, int cols, boolean [] visited) { return i >= 0 && i < rows && j >= 0 && j < cols && !visited[i * cols + j] && getDigitSum(i) + getDigitSum(j) <= threshold; } private int getDigitSum (int i) { int res = 0 ; while (i > 0 ) { res += i % 10 ; i /= 10 ; } return res; } }
14. 剪绳子 题目描述 给你一根长度为n的绳子,请把绳子剪成整数长的m段(m、n都是整数,n>1并且m>1),每段绳子的长度记为k[0],k[1],…,k[m]。请问k[0]xk[1]x…xk[m]可能的最大乘积是多少?例如,当绳子的长度是8时,我们把它剪成长度分别为2、3、3的三段,此时得到的最大乘积是18。
输入输出 大致思路 动态规划:
贪心算法:
证明:当 n >= 5 时,3(n - 3) - n = 2n - 9 > 0,且 2(n - 2) - n = n - 4 > 0。因此在 n >= 5 的情况下,将绳子剪成一段为 2 或者 3,得到的乘积会更大。又因为 3(n - 3) - 2(n - 2) = n - 5 >= 0,所以剪成一段长度为 3 比长度为 2 得到的乘积更大。
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 public class Solution { public int cutRope (int target) { if (target < 2 ){ return 0 ; } if (target == 2 ){ return 1 ; } if (target == 3 ){ return 2 ; } int [] products = new int [target + 1 ]; products[0 ] = 0 ; products[1 ] = 1 ; products[2 ] = 2 ; products[3 ] = 3 ; int max = 0 ; for (int i = 4 ; i <= target; i++){ max = 0 ; for (int j = 1 ;j <= i/2 ; j++){ int product = products[j] * products[i-j]; if (max < product){ max = product; products[i] = max; } } } return products[target]; } } public class Solution { public int cutRope (int target) { if (target < 2 ){ return 0 ; } if (target == 2 ){ return 1 ; } if (target == 3 ){ return 2 ; } int timesOf3 = target / 3 ; if (target - timesOf3 * 3 == 1 ){ timesOf3--; } int timesOf2 = (target - timesOf3 * 3 ) / 2 ; return (int )(Math.pow(3 , timesOf3)) * (int )(Math.pow(2 , timesOf2)); } }
15.二进制中1的个数 题目描述 输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中 1 的个数。
大致思路 把一个整数减一并与它原来本身相与 能够把最右边的一位1变成0
以上操作可以做几次 则原数字中有多少个1
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class Solution { public int hammingWeight (int n) { int count = 0 ; while (n != 0 ){ ++count; n = (n - 1 ) & n; } return count; } }
16.数值的整数次方 题目描述 给定一个 double 类型的浮点数 base 和 int 类型的整数 exponent,求 base 的 exponent 次方。
大致思路 1.当指数为负时取其绝对值算出结果之后取倒数
2.用公式将次方分割成奇数和偶数 再用递归逐步分割
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class Solution { public double Power (double base, int exponent) { double result = 1.0 ; int n = Math.abs(exponent); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ result *= base; } return exponent<0 ? 1.0 /result: result; } } class Solution { public double myPow (double x, int n) { long num = n; return pow(x, num); } private double pow (double x, long n) { if (n == 0 ) return 1 ; if (n == 1 ) return x; boolean isNegative = false ; if (n < 0 ){ n = -n; isNegative = true ; } double pow_result = pow(x * x, n / 2 ); if (n % 2 != 0 ){ pow_result *= x; } return isNegative?1 / pow_result: pow_result; } }
17.打印从1到最大的n位数 题目描述 输入数字 n,按顺序打印出从 1 到最大的 n 位十进制数。比如输入 3,则打印出 1、2、3 一直到最大的 3 位数 999。
输入输出 大致思路 print1ToMaxOfNDigits用于将每一位从1加到9
printNumber用于将每一位打印出来(注:遇到099时从第二位开始打印)
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public void print1ToMaxOfNDigits (int n) { if (n <= 0 ) return ; char [] number = new char [n]; print1ToMaxOfNDigits(number, 0 ); } private void print1ToMaxOfNDigits (char [] number, int digit) { if (digit == number.length) { printNumber(number); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { number[digit] = (char ) (i + '0' ); print1ToMaxOfNDigits(number, digit + 1 ); } } private void printNumber (char [] number) { int index = 0 ; while (index < number.length && number[index] == '0' ) index++; while (index < number.length) System.out.print(number[index++]); System.out.println(); } class Solution { public int [] printNumbers(int n) { int max = (int )Math.pow(10 , n); int [] ans = new int [max - 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= max - 1 ; i++){ ans[i - 1 ] = i; } return ans; } }
18.删除链表的节点 18.1删除链表节点(给定指针) 题目描述 O(1)时间删除链表节点
大致思路 将节点的值赋值给他的前一个节点 再修改next指针
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public ListNode deleteNode (ListNode head, ListNode tobeDelete) { if (head == null || tobeDelete == null ) return null ; if (tobeDelete.next != null ) { ListNode next = tobeDelete.next; tobeDelete.val = next.val; tobeDelete.next = next.next; } else { if (head == tobeDelete) head = null ; else { ListNode cur = head; while (cur.next != tobeDelete) cur = cur.next; cur.next = null ; } } return head; }
18.2删除链表中的节点(给定值) 输入输出 输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 5
大致思路 还是双指针
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public ListNode deleteNode (ListNode head, int val) { if (head.val == val) return head.next; ListNode pre = head, cur = head.next; while (cur != null && cur.val != val) { pre = cur; cur = cur.next; } pre.next = cur.next; return head; } }
18.3删除链表中重复的节点 输入输出 1 2 输入:1->2->3->3->4->4->5 输出:1->2->5
大致思路 设置两个指针pre和cur pre指向cur的前一个指针 cur过虑重复值
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 public class Solution { public ListNode deleteDuplication (ListNode pHead) { if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null ) { return pHead; } ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = pHead; while (cur != null ) { if (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == cur.val) { int val = cur.val; while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == val) { cur = cur.next; } if (pre == null ){ pHead = cur.next; } else { pre.next = cur.next; } } else { pre = cur; } cur = cur.next; } return pHead; } } public ListNode deleteDuplication (ListNode pHead) { if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null ) return pHead; ListNode next = pHead.next; if (pHead.val == next.val) { while (next != null && pHead.val == next.val) next = next.next; return deleteDuplication(next); } else { pHead.next = deleteDuplication(pHead.next); return pHead; } }
19.正则表达式匹配 题目描述 1 2 3 4 请实现一个函数用来匹配包含'. ' 和'*' 的正则表达式。 模式中的字符'.' 表示任意一个字符,而'*' 表示它前面的字符可以出现任意次(含0次)。 在本题中,匹配是指字符串的所有字符匹配整个模式。 例如,字符串"aaa" 与模式"a.a" 和"ab*ac*a" 匹配,但与"aa.a" 和"ab*a" 均不匹配。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 输入: s = "aa" p = "a" 输出: false 解释: "a" 无法匹配 "aa" 整个字符串。 输入: s = "aa" p = "a*" 输出: true 解释: 因为 '*' 代表可以匹配零个或多个前面的那一个元素, 在这里前面的元素就是 'a' 。因此,字符串 "aa" 可被视为 'a' 重复了一次。 输入: s = "ab" p = ".*" 输出: true 解释: ".*" 表示可匹配零个或多个('*' )任意字符('.' )。 输入: s = "aab" p = "c*a*b" 输出: true 解释: 因为 '*' 表示零个或多个,这里 'c' 为 0 个, 'a' 被重复一次。因此可以匹配字符串 "aab" 。 输入: s = "mississippi" p = "mis*is*p*." 输出: false
大致思路 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 def ideas (): if (两串中有一串为空): return false; if (两串都遍历完): return true; if (模式串第二位是 * 时): if (模式串与字符串第一位相同 或 模式串第一位是 . ): 递归比较(i,j+2 ) || (i+1 ,j) || (i+1 ,j+2 ); else : 递归比较(i,j+2 ); if (模式串与字串的第一位相同 或 模式串第一位是 . ): 递归比较(i+1 ,j+1 ); return false;
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public class Solution {public boolean match (char [] str, char [] pattern) { if (str == null || pattern == null ){ return false ; } else { return match(str, 0 , pattern, 0 ); } } private boolean match (char [] str, int i, char [] pattern, int j) { if (j == pattern.length) return str.length == i; if (j < pattern.length - 1 && pattern[j + 1 ] == '*' ) { if (str.length != i && (str[i] == pattern[j] || pattern[j] == '.' )) return match(str,i,pattern,j + 2 ) || match(str,i + 1 ,pattern,j) || match(str,i + 1 ,pattern,j + 2 ); else return match(str,i,pattern,j + 2 ); } if (str.length != i && (str[i] == pattern[j] || pattern[j] == '.' )) return match(str,i + 1 ,pattern,j + 1 ); return false ; } }
20.表示数值的字符串 题目描述 1 2 3 请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数) 例如,字串"+100" 、"5e2" 、"-123" 、"3.1416" 、"0123" 及"-1E-16" 都表示数值 但"12e" 、"1a3.14" 、"1.2.3" 、"+-5" 及"12e+5.4" 都不是
大致思路 1 2 scanUnsignedInteger(): 判断有无0 ~ 9的数字 scanInteger(): 判断以+ 或 -起始的数字中是否有1 ~ 9的数字
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 public class Solution { private int index = 0 ; public boolean isNumeric (char [] str) { if (str == null || str.length < 1 ) { return false ; } boolean flag = scanInteger(str); if (index < str.length && str[index] == '.' ) { index++; flag = scanUnsignedInteger(str) || flag; } if (index < str.length && (str[index] == 'e' || str[index] == 'E' )) { index++; flag = scanInteger(str) && flag; } return flag && index == str.length; } private boolean scanInteger (char [] str) { if (index < str.length && (str[index] == '+' || str[index] == '-' )) { index++; } return scanUnsignedInteger(str); } private boolean scanUnsignedInteger (char [] str) { int start = index; while (index < str.length && str[index] >= '0' && str[index] <= '9' ) { index++; } return index > start; } } class Solution { int i = 0 ; public boolean isNumber (String s) { if (s == null || s.length() == 0 ) return false ; s = s.trim(); boolean A = scanInteger(s), B = false , C = false ; if (i < s.length() && s.charAt(i) == '.' ) { i++; B = scanUnsignedInteger(s); } if (i < s.length() && (s.charAt(i) == 'e' || s.charAt(i) == 'E' )) { i++; C = scanInteger(s); if (C == false ) return false ; } return i == s.length() && (A || B); } private boolean scanInteger (String s) { if (i < s.length() && (s.charAt(i) == '+' || s.charAt(i) == '-' )) i++; return scanUnsignedInteger(s); } private boolean scanUnsignedInteger (String s) { int start = i; while (i < s.length() && s.charAt(i) >= '0' && s.charAt(i) <= '9' ) { i++; } return i > start; } }
21.调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面 题目描述 输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分。
大致思路 需要相对位置不变时 用冒泡排序
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public class Solution { public void reOrderArray (int [] nums) { int N = nums.length; for (int i = N - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) { for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (isEven(nums[j]) && !isEven(nums[j + 1 ])) { swap(nums, j, j + 1 ); } } } } private boolean isEven (int x) { return x % 2 == 0 ; } private void swap (int [] nums, int i, int j) { int t = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = t; } } class Solution { public int [] exchange(int [] nums) { int i = 0 , j = nums.length - 1 , tmp; while (i < j) { while (i < j && (nums[i] & 1 ) == 1 ) i++; while (i < j && (nums[j] & 1 ) == 0 ) j--; tmp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = tmp; } return nums; } }
22.链表中倒数第k个节点 题目描述 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题从1开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第1个节点。例如,一个链表有6个节点,从头节点开始,它们的值依次是1、2、3、4、5、6。这个链表的倒数第3个节点是值为4的节点。
大致思路 双指针 前后一起移动(注意代码的鲁棒性)
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public class Solution { public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode head,int k) { if (head == null || k == 0 ){ return null ; } int length = 0 ; ListNode count = head; while (count != null ){ count = count.next; length++; } if (k > length){ return null ; } ListNode p1 = head; while (k-- > 0 && p1 != null ){ p1 = p1.next; } ListNode p2 = head; while (p1 != null ){ p2 = p2.next; p1 = p1.next; } return p2; } }
23.链表中环的入口节点 题目描述 给一个链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,输出null。
大致思路
先利用快慢指针。若能相遇,说明存在环,且相遇点一定是在环上;若没有相遇,说明不存在环,返回 null。
固定当前相遇点,用一个指针继续走,同时累积结点数。计算出环的结点个数 cnt。
指针 p1 先走 cnt 步,p2 指向链表头部,之后 p1,p2 同时走,相遇时,相遇点一定是在环的入口处。因为 p1 比 p2 多走了环的一圈。
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 public class Solution { public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop (ListNode pHead) { if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null ){ return null ; } ListNode fast = pHead; ListNode slow = pHead; boolean isLoop = false ; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == slow){ isLoop = true ; break ; } } if (!isLoop){ return null ; } ListNode cur = slow.next; int count = 1 ; while (cur != slow){ cur = cur.next; count++; } ListNode p1 = pHead; while (count > 0 ){ p1 = p1.next; count--; } ListNode p2 = pHead; while (p1 != p2){ p1 = p1.next; p2 = p2.next; } return p2; } }
24.反转链表 题目描述 定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
输入输出 1 2 输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
大致思路 递归 or 双指针迭代
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ){ return head; } ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next); head.next.next = head; head.next = null ; return newHead; } } class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = head; ListNode temp = null ; while (cur != null ){ temp = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; } }
25.合并两个排序的链表/数组 题目描述 (数组)给定两个排序后的数组 A 和 B,其中 A 的末端有足够的缓冲空间容纳 B。 编写一个方法,将 B 合并入 A 并排序。初始化 A 和 B 的元素数量分别为 m 和 n。
大致思路 merge 常规套路
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 class Solution { public void merge (int [] A, int m, int [] B, int n) { int i = m - 1 ; int j = n - 1 ; int k = m + n - 1 ; while (i >= 0 && j >= 0 ){ if (A[i] > B[j]){ A[k--] = A[i--]; } else { A[k--] = B[j--]; } } while (j >= 0 ){ A[k--] = B[j--]; } } } class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { if (l1 == null ) return l2; if (l2 == null ) return l1; ListNode head = null ; if (l1.val <= l2.val){ l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2); return l1; } else { l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next); return l2; } } } public class Solution { public ListNode Merge (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { if (list1 == null ) { return list2; } if (list2 == null ) { return list1; } ListNode dummy = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode cur = dummy; ListNode p1 = list1; ListNode p2 = list2; while (p1 != null && p2 != null ) { if (p1.val < p2.val) { ListNode t = p1.next; cur.next = p1; p1.next = null ; p1 = t; } else { ListNode t = p2.next; cur.next = p2; p2.next = null ; p2 = t; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = p1 == null ? p2 : p1; return dummy.next; } }
26.树的子结构 题目描述 输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 例如: 给定的树 A: 3 / \ 4 5 / \ 1 2 给定的树 B: 4 / 1 返回 true ,因为 B 与 A 的一个子树拥有相同的结构和节点值。
大致思路 1 2 isAhasB()查找A中是否有和B一样的节点R isSubStructure()查找A中以R为根节点的子树是不是和B一样结构
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public boolean isSubStructure (TreeNode A, TreeNode B) { if (A == null || B == null ){ return false ; } return isAhasB(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B) || isSubStructure(A.right, B); } private boolean isAhasB (TreeNode A, TreeNode B) { if (B == null ){ return true ; } if (A == null ){ return false ; } if (A.val != B.val){ return false ; } return isAhasB(A.left, B.left) && isAhasB(A.right, B.right); } }
27.二叉树的镜像 题目描述 操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 二叉树的镜像定义:源二叉树 8 / \ 6 10 / \ / \ 5 7 9 11 镜像二叉树 8 / \ 10 6 / \ / \ 11 9 7 5
大致思路 递归
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public TreeNode mirrorTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return null ; } TreeNode temp = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = temp; mirrorTree(root.left); mirrorTree(root.right); return root; } }
28.对称的二叉树 题目描述 请实现一个函数,用来判断一棵二叉树是不是对称的。如果一棵二叉树和它的镜像一样,那么它是对称的。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 输出:true 输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 输出:false
大致思路 1 一棵树的前序遍历等于他对称树的反前序遍历(根右左)
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return true ; } return isSymmetric(root, root); } public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode pRoot1, TreeNode pRoot2) { if (pRoot1 == null && pRoot2 == null ){ return true ; } if (pRoot1 == null || pRoot2 == null ){ return false ; } if (pRoot1.val != pRoot2.val){ return false ; } return isSymmetric(pRoot1.left, pRoot2.right) && isSymmetric(pRoot1.right, pRoot2.left); } }
29.顺时针打印矩阵 题目描述 4乘4 的矩阵数字从1到16 顺时针打印
输入输出 矩阵顺时针打印结果为:1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 16, 15, 14, 13, 9, 5, 6, 7, 11, 10
大致思路 先左到右 再上到下 再右到左 再下到上
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix (int [][] matrix) { ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList <>(); int r1 = 0 , r2 = matrix.length - 1 , c1 = 0 , c2 = matrix[0 ].length - 1 ; while (r1 <= r2 && c1 <= c2) { for (int i = c1; i <= c2; i++) ret.add(matrix[r1][i]); for (int i = r1 + 1 ; i <= r2; i++) ret.add(matrix[i][c2]); if (r1 != r2) for (int i = c2 - 1 ; i >= c1; i--) ret.add(matrix[r2][i]); if (c1 != c2) for (int i = r2 - 1 ; i > r1; i--) ret.add(matrix[i][c1]); r1++; r2--; c1++; c2--; } return ret; } class Solution { public int [] spiralOrder(int [][] matrix) { int m = matrix.length; if (m==0 ){ return new int []{}; } int n = matrix[0 ].length; int top = 0 , bot = m-1 , left = 0 , right = n-1 ; int cnt = 0 ; int [] res = new int [m*n]; while (top<=bot&&left<=right){ for (int j=left;j<=right;j++){ res[cnt++] = matrix[top][j]; } top++; for (int i=top;i<=bot;i++){ res[cnt++] = matrix[i][right]; } right--; for (int j=right;j>=left&&top<=bot;j--){ res[cnt++] = matrix[bot][j]; } bot--; for (int i=bot;i>=top&&left<=right;i--){ res[cnt++] = matrix[i][left]; } left++; } return res; } }
30.包含min函数的栈 题目描述 定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈的最小元素的 min 函数在该栈中,调用 min、push 及 pop 的时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MinStack minStack = new MinStack(); minStack.push(-2); minStack.push(0); minStack.push(-3); minStack.min(); --> 返回 -3. minStack.pop(); minStack.top(); --> 返回 0. minStack.min(); --> 返回 -2.
大致思路 设置两个栈 一个存数据 一个存最小值 保证后者栈顶是当前栈内数据的最小值
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 import java.util.Stack;public class Solution { private Stack<Integer> dataStack = new Stack <>(); private Stack<Integer> minStack = new Stack <>(); public void push (int node) { dataStack.push(node); minStack.push(minStack.isEmpty()? node: Math.min(minStack.peek(), node)); } public void pop () { dataStack.pop(); minStack.pop(); } public int top () { return dataStack.peek(); } public int min () { return minStack.peek(); } } class MinStack { Stack<Integer> dataStack,minStack; public MinStack () { dataStack = new Stack <>(); minStack = new Stack <>(); } public void push (int x) { dataStack.add(x); if (minStack.isEmpty() || x <= minStack.peek()){ minStack.add(x); } } public void pop () { if (dataStack.pop().equals(minStack.peek())){ minStack.pop(); } } public int top () { return dataStack.peek(); } public int min () { return minStack.peek(); } }
31.栈的压入 弹出序列 题目描述 输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如,序列 {1,2,3,4,5} 是某栈的压栈序列,序列 {4,5,3,2,1} 是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但 {4,3,5,1,2} 就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 输入:pushed = [1,2,3,4,5], popped = [4,5,3,2,1] 输出:true 输入:pushed = [1,2,3,4,5], popped = [4,3,5,1,2] 输出:false
大致思路 取一个栈模拟操作 如果有弹出序列中的元素则pop 如果最后栈为空则序列正确
java代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import java.util.Stackclass Solution { public boolean validateStackSequences (int [] pushed, int [] popped) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); int i = 0 ; for (int num : pushed){ stack.push(num); while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == popped[i]){ stack.pop(); i++; } } return stack.isEmpty(); } }
32.从上往下打印二叉树 32.1从上往下打印二叉树 题目描述 从上往下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同层节点从左至右打印。(层次遍历)
输入输出 三层满二叉树输出1 2 3 4 5 6 7
大致思路 层次遍历
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.Queue;public class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> PrintFromTopToBottom (TreeNode root) { Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList <>(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int count = queue.size(); while (count-- > 0 ){ TreeNode t = queue.poll(); if (t == null ){ continue ; } ret.add(t.val); queue.add(t.left); queue.add(t.right); } } return ret; } }
32.2 从上到下打印二叉树 题目描述 从上到下按层打印二叉树,同一层的节点按从左到右的顺序打印,每一层打印到一行。
输入输出 分行打印
大致思路 设置变量按每层打印完循环一次打印一次设置一个tmp存储新的数据
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (root != null ) queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = queue.size(); i > 0 ; i--){ TreeNode t = queue.poll(); tmp.add(t.val); if (t.left != null ) queue.add(t.left); if (t.right != null ) queue.add(t.right); } res.add(tmp); } return res; } }
32.3按之字形顺序打印二叉树 题目描述 请实现一个函数按照之字形打印二叉树,即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右至左的顺序打印,第三行按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推。
大致思路 层序遍历+双端队列/两个栈/直接用变量标记奇数行偶数行用Collections反转保存
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); if (root != null ) queue.add(root); boolean reverse = false ; while (!queue.isEmpty()){ ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); int cnt = queue.size(); while (cnt-- > 0 ){ TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node == null ) continue ; list.add(node.val); queue.add(node.left); queue.add(node.right); } if (reverse) Collections.reverse(list); reverse = !reverse; if (!list.isEmpty()) res.add(list); } return res; } }
33.二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列 题目描述 输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。如果是则输出Yes,否则输出No。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 5 / \ 2 6 / \ 1 3 输入: [1,6,3,2,5] 输出: false 输入: [1,3,2,6,5] 输出: true
大致思路 后序遍历中最后一个值是根节点 可分割前边节点值为 小于他 和 大于他 两部分 在这个情况下继续不断递归划分
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class Solution { public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST (int [] sequence) { if (sequence == null || sequence.length == 0 ) return true ; return verify(sequence, 0 , sequence.length - 1 ); } private boolean verify (int [] sequence, int first, int last) { if (last - first <= 1 ) return true ; int rootval = sequence[last]; int index = first; while (index < last && sequence[index] <= rootval){ index++; } for (int i = index; i < last; i++){ if (sequence[i] < rootval) return false ; } return verify(sequence, first, index-1 ) && verify(sequence, index, last-1 ); } }
34.二叉树中和为某一值的路径 题目描述 输入一棵二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中节点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。从树的根节点开始往下一直到叶节点所经过的节点形成一条路径。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 5 / \ 4 8 / / \ 11 13 4 / \ / \ 7 2 5 1 [ [5,4,11,2], [5,8,4,5] ]
大致思路 前序遍历+回溯法 设置path中数值和是否等于target 不能的话回溯到上一个结点访问其他子节点
java代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { LinkedList<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root, int sum) { recur(root, sum); return res; } private void recur (TreeNode root, int target) { if (root == null ) return ; path.add(root.val); target -= root.val; if (root.left == null && root.right == null && target == 0 ) res.add(new LinkedList (path)); recur(root.left, target); recur(root.right, target); path.removeLast(); } }
35.复杂链表的复制 题目描述 输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针random指向一个随机节点),请对此链表进行深拷贝,并返回拷贝后的头结点。(注意,输出结果中请不要返回参数中的节点引用,否则判题程序会直接返回空)
大致思路 1.先把所有链表节点再原始节点后边复制一遍
在复制出来的新节点上建立random连接
将链表拆分开来
2.使用HashMap键值对存储再连接
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 class Node { int val; Node next; Node random; public Node (int val) { this .val = val; this .next = null ; this .random = null ; } } class Solution { public Node copyRandomList (Node head) { if (head == null ){ return null ; } copyNode(head); randomDirect(head); return reList(head); } private void copyNode (Node head) { while (head != null ){ Node nextNode = head.next; Node newNode = new Node (head.val); head.next = newNode; newNode.next = nextNode; head = nextNode; } } private void randomDirect (Node head) { while (head != null ){ Node nextNode = head.next; if (head.random != null ){ Node direct = head.random; nextNode.random = direct.next; } head = nextNode.next; } } private Node reList (Node head) { Node newNode = head.next; Node newHead = newNode; head.next = newNode.next; head = head.next; while (head != null ){ newNode.next = head.next; head.next = head.next.next; head = head.next; newNode = newNode.next; } return newHead; } } class Solution { public Node copyRandomList (Node head) { HashMap<Node, Node> hashmap = new HashMap <>(); Node cur = head; while (cur != null ){ hashmap.put(cur, new Node (cur.val)); cur = cur.next; } cur = head; while (cur != null ){ hashmap.get(cur).next = hashmap.get(cur.next); hashmap.get(cur).random = hashmap.get(cur.random); cur = cur.next; } return hashmap.get(head); } }
36.二叉搜索树与双向链表 题目描述 输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的循环双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的节点,只能调整树中节点指针的指向。
大致思路
二叉搜索树的中序遍历是递增序列
先中序遍历 再设置双向链表的左右指针
最后设置第一个节点和最后一个节点的左右指针
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution { Node pre, head; public Node treeToDoublyList (Node root) { if (root == null ) return null ; inOrder(root); head.left = pre; pre.right = head; return head; } public void inOrder (Node cur) { if (cur == null ) return ; inOrder(cur.left); if (pre != null ) pre.right = cur; else head = cur; cur.left = pre; pre = cur; inOrder(cur.right); } }
39.数组中出现次数超过一半的数字 题目描述 数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。
输入输出 1 2 输入: [1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 2, 5, 4, 2] 输出: 2
大致思路 多数投票问题,可以利用 Boyer-Moore Majority Vote Algorithm 来解决这个问题,使得时间复杂度为 O(N)。
使用 cnt 来统计一个元素出现的次数,当遍历到的元素和统计元素相等时,令 cnt++,否则令 cnt–。如果前面查找了 i 个元素,且 cnt == 0,说明前 i 个元素没有 majority,或者有 majority,但是出现的次数少于 i / 2 ,因为如果多于 i / 2 的话 cnt 就一定不会为 0 。此时剩下的 n - i 个元素中,majority 的数目依然多于 (n - i) / 2,因此继续查找就能找出 majority。
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int majorityElement (int [] nums) { int majority = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 , cnt = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++){ cnt = nums[i] == majority?cnt + 1 : cnt - 1 ; if (cnt == 0 ){ cnt = 1 ; majority = nums[i]; } } int cnt = 0 ; for (int value : nums){ if (value == majority){ cnt++; } } return cnt > (nums.length / 2 ) ? majority : 0 ; } }
40.最小的k个数 题目描述 输入整数数组 arr ,找出其中最小的 k 个数。例如,输入4、5、1、6、2、7、3、8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1、2、3、4。
大致思路
使用快速排序(注意找前 K 大/前 K 小问题不需要对整个数组进行 O(NlogN)O(NlogN) 的排序!
堆排序(java中有现成的 PriorityQueue )
二叉搜索树
数量有限时 直接计数排序
神仙BFPRT算法
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 class Solution { public int [] getLeastNumbers(int [] arr, int k) { if (k == 0 || arr.length == 0 ) return new int [0 ]; return QuickSort(arr, 0 , arr.length - 1 , k-1 ); } private int [] QuickSort(int [] arr, int low, int high, int k){ int pivot = partition(arr, low, high); if (pivot == k){ return Arrays.copyOf(arr, pivot + 1 ); } return pivot < k? QuickSort(arr, pivot + 1 , high, k) : QuickSort(arr,low, pivot - 1 , k); } private int partition (int [] nums, int low, int high) { int pivot = nums[low]; while (low < high){ while (low < high && nums[high] >= pivot){ --high; } nums[low] = nums[high]; while (low < high && nums[low] <= pivot){ ++low; } nums[high] = nums[low]; } nums[low] = pivot; return low; } } class Solution { public int [] getLeastNumbers(int [] arr, int k) { if (k == 0 || arr.length == 0 ) { return new int [0 ]; } Queue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue <>((v1, v2) -> v2 - v1); for (int num: arr) { if (pq.size() < k) { pq.offer(num); } else if (num < pq.peek()) { pq.poll(); pq.offer(num); } } int [] res = new int [pq.size()]; int idx = 0 ; for (int num: pq) { res[idx++] = num; } return res; } }
42.连续子数组的最大和 题目描述 输入一个整型数组,数组里有正数也有负数。数组中的一个或连续多个整数组成一个子数组。求所有子数组的和的最大值。
要求时间复杂度为O(n)。
输入输出 1 2 3 输入: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4] 输出: 6 解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。
大致思路
状态定义: 设动态规划列表 dp,dp[i] 代表以元素nums[i]为结尾的连续子数组最大和。
为何定义最大和dp[i]中必须包含元素nums[i]:保证dp[i] 递推到dp[i+1]的正确性;如果不包含nums[i] ,递推时则不满足题目的连续子数组 要求。
转移方程: 若dp[i-1] ≤ 0 ,说明dp[i-1]对dp[i]产生负贡献 那dp[i-1] + nums[i]还不如nums[i]本身大。
当 dp[i - 1] > 0时:执行dp[i] = dp[i-1] + nums[i] ;
当 dp[i - 1] <= 0时:执行 dp[i] = nums[i];
初始状态: dp[0] = nums[0],即以 nums[0]结尾的连续子数组最大和为 nums[0]。
返回值: 返回 dp列表中的最大值,代表全局最大值。
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ) return 0 ; int greatestSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int sum = 0 ; for (int value : nums){ sum = sum < 0 ? value: sum + value; greatestSum = Math.max(greatestSum, sum); } return greatestSum; } }
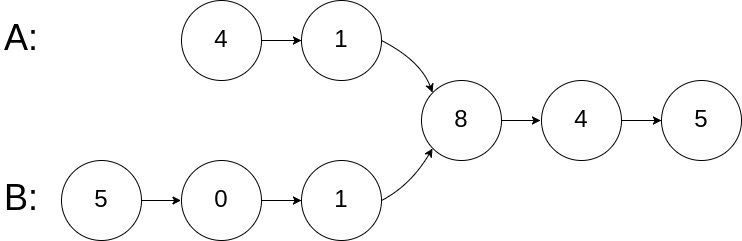
52.两个链表的第一个公共节点 题目描述 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共节点。
输入输出
1 2 3 输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Reference of the node with value = 8 输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
大致思路 双指针同时向后移动 每当链表A上的指针走完就从B开始 链表B上的指针走完就从A开始 相遇节点=公共节点
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if (headA == null || headB == null ){ return null ; } ListNode node1 = headA; ListNode node2 = headB; while (node1 != node2){ node1 = node1 != null ? node1.next: headB; node2 = node2 != null ? node2.next:headA; } return node1; } }
54.二叉搜索树的第k大节点 题目描述 给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中第k大的节点。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 输入: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1 3 / \ 1 4 \ 2 输出: 4 输入: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3 5 / \ 3 6 / \ 2 4 / 1 输出: 4
大致思路 递归解析:
终止条件: 当节点 root 为空(越过叶节点),则直接返回;
递归右子树: 即 dfs(root.right) ;
三项工作:
提前返回: 若k=0 ,代表已找到目标节点,无需继续遍历,因此直接返回;
统计序号: 执行 k=k−1 (即从 k 减至 0 );
记录结果: 若 k = 0 ,代表当前节点为第 k 大的节点,因此记录 res=root.val;
递归左子树: 即dfs(root.left);
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { int res,k; public int kthLargest (TreeNode root, int k) { this .k = k; dfs(root); return res; } void dfs (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return ; dfs(root.right); if (k == 0 ) return ; if (--k == 0 ) res = root.val; dfs(root.left); } }
57.和为s的两个数字 57.1 题目描述 输入一个递增排序的数组和一个数字s,在数组中查找两个数,使得它们的和正好是s。如果有多对数字的和等于s,则输出任意一对即可。
输入输出 1 2 输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 输出:[2,7] 或者 [7,2]
大致思路 设置前后两个指针 一个在数组首部 一个在数组尾部 两个值相加
若小于所求和 则首部指针后移 若大于所求和 则尾部指针前移
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { int i = 0 , j = nums.length - 1 ; while (i < j) { int s = nums[i] + nums[j]; if (s < target) i++; else if (s > target) j--; else return new int [] { nums[i], nums[j] }; } return new int [0 ]; } }
57.2 题目描述 输入一个正整数 target ,输出所有和为 target 的连续正整数序列(至少含有两个数)。
序列内的数字由小到大排列,不同序列按照首个数字从小到大
输入输出 1 2 输入:target = 9 输出:[[2,3,4],[4,5]]
大致思路
当窗口的和小于 target 的时候,窗口的和需要增加,所以要扩大窗口,窗口的右边界向右移动
当窗口的和大于 target 的时候,窗口的和需要减少,所以要缩小窗口,窗口的左边界向右移动
当窗口的和恰好等于 target 的时候,我们需要记录此时的结果。设此时的窗口为 [i, j[i,j),那么我们已经找到了一个 ii 开头的序列,也是唯一一个 ii 开头的序列,接下来需要找 i+1i+1 开头的序列,所以窗口的左边界要向右移动
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import java.util.ArrayList;public class Solution { public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > FindContinuousSequence(int sum) { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList <>(); int start = 1 ,end = 2 ; int curSum = 3 ; int middle = (1 + sum)/2 ; while (start < middle){ if (curSum < sum){ end++; curSum += end; } else if (curSum > sum){ curSum -= start; start++; } else { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = start; i <= end; i++){ list.add(i); } ret.add(list); curSum -= start; start++; end++; curSum += end; } } return ret; } } public int [][] findContinuousSequence(int target) { int i = 1 ; int j = 1 ; int sum = 0 ; List<int []> res = new ArrayList <>(); while (i <= target / 2 ) { if (sum < target) { sum += j; j++; } else if (sum > target) { sum -= i; i++; } else { int [] arr = new int [j-i]; for (int k = i; k < j; k++) { arr[k-i] = k; } res.add(arr); sum -= i; i++; } } return res.toArray(new int [res.size()][]); }
59.队列的最大值 59.1滑动窗口的最大值 题目描述 给定一个数组 nums 和滑动窗口的大小 k,请找出所有滑动窗口里的最大值。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 输入: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7] 和 k = 3 输出: [3,3,5,5,6,7] 滑动窗口的位置 最大值 [1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3 1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3 1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5 1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5 1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6 1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
大致思路 使用双端队列进行操作(队列中不存值 存数组下标 )
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 class Solution { public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) { if (nums == null || k < 1 || nums.length < k || nums.length == 0 ) { return new int [0 ]; } int index = 0 ; int [] res = new int [nums.length - k + 1 ]; LinkedList<Integer> qMax = new LinkedList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { while (!qMax.isEmpty() && nums[qMax.peekLast()] <= nums[i]) { qMax.pollLast(); } qMax.addLast(i); if (qMax.peekFirst() == (i - k)) { qMax.pollFirst(); } if (i >= (k - 1 )) { res[index++] = nums[qMax.peekFirst()]; } } return res; } } import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Deque;import java.util.LinkedList;public class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows (int [] num, int size) { ArrayList<Integer> reList = new ArrayList <>(); if (num == null || num.length < size || size < 1 ) { return reList; } Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < num.length; i++) { while (!deque.isEmpty() && num[deque.getLast()] <= num[i]) { deque.pollLast(); } while (!deque.isEmpty() && (i - deque.getFirst() + 1 > size)) { deque.pollFirst(); } deque.add(i); if (!deque.isEmpty() && i + 1 >= size) { reList.add(num[deque.getFirst()]); } } return reList; } }
59.2队列的最大值 题目描述 1 2 3 4 请定义一个队列并实现函数 max_value 得到队列里的最大值 要求函数max_value、push_back 和 pop_front 的均摊时间复杂度都是O(1) 若队列为空,pop_front 和 max_value 需要返回 -1
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 输入: ["MaxQueue" ,"push_back" ,"push_back" ,"max_value" ,"pop_front" ,"max_value" ] [[],[1],[2],[],[],[]] 输出: [null,null,null,2,1,2] 输入: ["MaxQueue" ,"pop_front" ,"max_value" ] [[],[],[]] 输出: [null,-1,-1]
大致思路 维护一个队列和双端队列
队列用于操作 双端队列用于储存 队首到队尾值从大到小
java代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class MaxQueue { Queue<Integer> que; Deque<Integer> deq; public MaxQueue () { que = new LinkedList <>(); deq = new LinkedList <>(); } public int max_value () { return deq.size()>0 ?deq.peek():-1 ; } public void push_back (int value) { que.offer(value); while (deq.size()>0 && deq.peekLast()<value){ deq.pollLast(); } deq.offerLast(value); } public int pop_front () { int tmp = que.size()>0 ?que.poll():-1 ; if (deq.size()>0 && tmp == deq.peek()){ deq.poll(); } return tmp; } }
60.n个骰子的点数 题目描述 把n个骰子扔在地上,所有骰子朝上一面的点数之和为s。输入n,打印出s的所有可能的值出现的概率。
你需要用一个浮点数数组返回答案,其中第 i 个元素代表这 n 个骰子所能掷出的点数集合中第 i 小的那个的概率。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 输入: 1 输出: [0.16667,0.16667,0.16667,0.16667,0.16667,0.16667] 输入: 2 输出: [0.02778,0.05556,0.08333,0.11111,0.13889,0.16667,0.13889,0.11111,0.08333,0.05556,0.02778]
大致思路 一个leetcode里不错的解析
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public double [] twoSum(int n) { double pre[]= {1 /6d , 1 /6d , 1 /6d , 1 /6d , 1 /6d , 1 /6d }; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++){ double tmp[] = new double [5 * i + 1 ]; for (int j = 0 ; j < pre.length; j++){ for (int x = 0 ; x < 6 ; x++){ tmp[j+x] += pre[j] / 6 ; } } pre = tmp; } return pre; } }
61.扑克牌中的顺子 题目描述 从扑克牌中随机抽5张牌,判断是不是一个顺子,即这5张牌是不是连续的。2~10为数字本身,A为1,J为11,Q为12,K为13,而大、小王为 0 ,可以看成任意数字。A 不能视为 14。
输入输出 1 2 3 4 输入: [1,2,3,4,5] 输出: True 输入: [0,0,1,2,5] 输出: True
大致思路 五张是顺子必须满足以下两个条件:
除大小王外,所有牌 无重复 ;
设此 55 张牌中最大的牌为 max ,最小的牌为 min (大小王除外),则需满足:
max - min < 5
Function1:集合Set+遍历
Function2:先对数组进行排序 计算数组中0的个数存在joker中 最后判断 nums[4] - nums[joker] < 5 ?
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 import java.util.Set;import java.util.HashSet;class Solution { public boolean isStraight (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ) return false ; Set<Integer> repeat = new HashSet <>(); int max = 0 ,min = 14 ; for (int num:nums){ if (num == 0 ) continue ; max = Math.max(num, max); min = Math.min(num, min); if (repeat.contains(num)) return false ; repeat.add(num); } return max - min < 5 ; } } class Solution { public boolean isStraight (int [] nums) { int joker = 0 ; Arrays.sort(nums); for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { if (nums[i] == 0 ) joker++; else if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1 ]) return false ; } return nums[4 ] - nums[joker] < 5 ; } }
63.圆圈中最后剩下的数字 题目描述 让小朋友们围成一个大圈。然后,随机指定一个数 m,让编号为 0 的小朋友开始报数。每次喊到 m-1 的那个小朋友要出列唱首歌,然后可以在礼品箱中任意的挑选礼物,并且不再回到圈中,从他的下一个小朋友开始,继续 0…m-1 报数 …. 这样下去 …. 直到剩下最后一个小朋友,可以不用表演。
输入输出 大致思路 代码使用循环的方法 可反推回来计算:
CSDN解析约瑟夫环(Josephus Problem)
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Solution { public int LastRemaining_Solution (int n, int m) { if (n == 0 ) return -1 ; if (n == 1 ) return 0 ; return (LastRemaining_Solution(n - 1 , m) + m ) % n; } } class Solution { public int lastRemaining (int n, int m) { int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++){ ans = (ans + m) % i; } return ans; } }
64.求1+2+…+n 题目描述 求1+2+3+…+n,要求不能使用乘除法、for、while、if、else、switch、case等关键字及条件判断语句(A?B:C)。
大致思路
使用递归解法最重要的是指定返回条件,但是本题无法直接使用 if 语句来指定返回条件。
条件与 && 具有短路原则,即在第一个条件语句为 false 的情况下不会去执行第二个条件语句。利用这一特性,将递归的返回条件取非然后作为 && 的第一个条件语句,递归的主体转换为第二个条件语句,那么当递归的返回条件为 true 的情况下就不会执行递归的主体部分,递归返回。
本题的递归返回条件为 n <= 0,取非后就是 n > 0;递归的主体部分为 sum += Sum_Solution(n - 1),转换为条件语句后就是 (sum += Sum_Solution(n - 1)) > 0。
最后一个>0是因为&&本身就是判断语句 必须返回boolean类型 所以使用>0
java实现 1 2 3 4 5 public int Sum_Solution (int n) { int sum = n; boolean b = (n > 0 ) && ((sum += Sum_Solution(n - 1 )) > 0 ); return sum; }